Android Display
Android can supports multiple screens, at least support two screens: a primary screen and a external screen, some hardware platform support three or more screens, but all these screens are presented in serial, which means all screens must be presented in a vsync period, the following figure shows the present sequence:
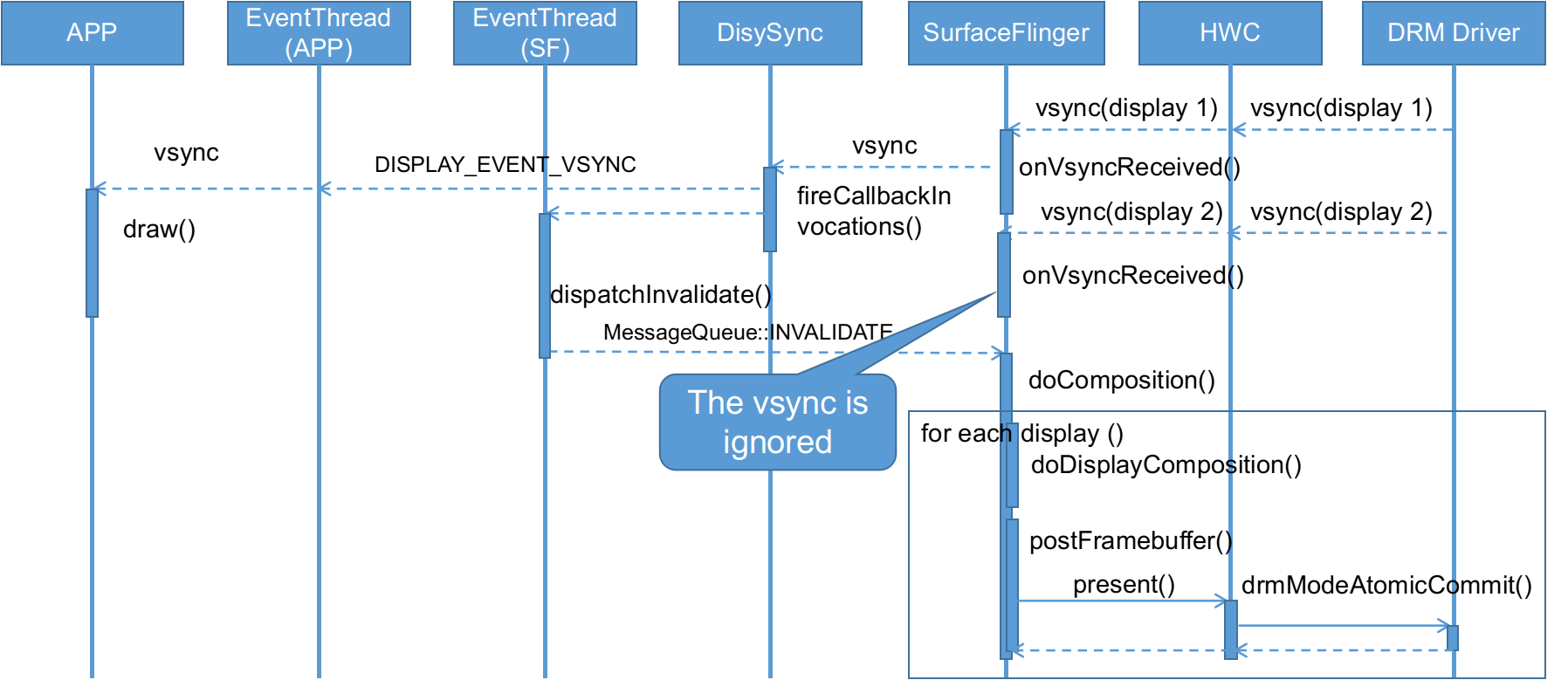
Figure 1: Display Present Sequence
The SurfaceFlinger::handleMessageRefresh() is used to handle refresh message, SurfaceFlinger::doComposition() is called in the function to do the graphic composition and present.
In kernel, drm driver do last hw plane composition and commit data to DU, the process of atomic commit is as follows:
int drm_mode_atomic_ioctl(struct drm_device *dev,
void *data, struct drm_file *file_priv)
-> ret = prepare_crtc_signaling(dev, state, arg, file_priv, &fence_state,
&num_fences);
-> fence_ptr = get_out_fence_for_crtc(crtc_state->state, crtc);
-> if (arg->flags & DRM_MODE_PAGE_FLIP_EVENT || fence_ptr) {
e = create_vblank_event(dev, arg->user_data);
crtc_state->event = e; }
-> int drm_atomic_commit(struct drm_atomic_state *state)
-> ret = drm_atomic_check_only(state);
-> if (config->funcs->atomic_check)
ret = config->funcs->atomic_check(state->dev, state);
-> int drm_atomic_helper_check(struct drm_device *dev,
struct drm_atomic_state *state)
-> ret = drm_atomic_helper_check_planes(dev, state);
-> plane->helper_private->atomic_check(plane, new_plane_state);
-> static void virtio_crtc_atomic_flush(struct drm_crtc *crtc,
struct drm_crtc_state *old_crtc_state)
-> config->funcs->atomic_commit(state->dev, state, false);
-> int drm_atomic_helper_commit(struct drm_device *dev,
struct drm_atomic_state *state, bool nonblock)
-> ret = drm_atomic_helper_setup_commit(state, nonblock);
-> for_each_oldnew_crtc_in_state(state, crtc, old_crtc_state, new_crtc_state, i) {
ret = stall_checks(crtc, nonblock); }
-> commit_tail(state);
-> funcs->atomic_commit_tail(old_state);
-> drm_atomic_helper_wait_for_flip_done(dev, state);
-> for_each_new_crtc_in_state(old_state, crtc, unused, i) {
ret = wait_for_completion_timeout(&commit->flip_done, 10 * HZ);}